CNC Machining Tolerances Explained: Key for Assuring Part Precision
CNC Machining Tolerances Explained: Key for Assuring Part Precision
Blog Article
CNC Machining Tolerances Explained: Key for Assuring Part Precision
Precision in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is of utmost importance. CNC tolerances refer to deviations in part dimensions that could alter its fit, function and longevity - these deviations directly affecting part fitment, useability and longevity. This article will highlight the essential role played by tolerances when it comes to CNC machining projects - their categories, applicable standards and best practices for selecting appropriate tolerances are discussed herein.
What Are CNC Machining Tolerances?
CNC machining tolerances refer to the permissible range of dimensional deviation from a part's nominal (or designed) dimensions. Tolerances establish boundaries within which parts can still function properly while being compatible with other components or systems. Without properly defined tolerances, parts could misfit, leading to malfunction, safety hazards, or increased wear.
Categories of CNC Machining Tolerances
CNC Machining tolerances can be divided into three general categories.
1. Dimensional Tolerances: These tolerances cover linear and angular dimensions such as length, width and diameter. These variances in size represent allowable variations that ensure compatible parts.
2. Geometric Tolerances: This category encompasses form and position tolerances such as straightness, flatness, circularity, parallelism, perpendicularity and symmetry. Geometric tolerances play an essential role in maintaining functional relationships between features ensuring they align properly and assemble according to plan.
3. Surface Roughness: Surface roughness tolerance refers to allowable micro-level variations in surface finish that impact friction and wear characteristics of parts, and precision is of particular importance in high-stress environments or parts that must interact directly with one or more other components.
Why Are CNC Machining Tolerances Necessary?
CNC machining tolerances play an integral part in determining part quality, functionality and assembly accuracy. Proper tolerancing offers various benefits:
Assembly Fit and Functionality: Accurate tolerances enable parts to fit together seamlessly in automotive, aerospace, or consumer electronics industries. When tolerances become improperly set however, components can loosen, bind, or misalign which has negative ramifications on overall product functionality and lifespan.
Consistency and Quality Control: Establishing standard tolerances reduces variation across production batches while tight tolerances minimize defects to ensure each part produced meets high-quality standards.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Management: Selecting optimal tolerances strikes a delicate balance between precision and production costs. While tight tolerances ensure high precision, they also require more advanced machinery and extend production times significantly. Deliberate tolerance selection helps lower production costs while upholding part quality.

CNC Machining Tolerance Standards
To maintain consistency and ensure part compatibility, various international standards outline general CNC machining tolerances. ISO 2768, DIN 7168, ASME Y14.5 and GB/T 1184-1996 are the most prevalent standards used.
1. ISO 2768 : International Tolerance Standard
ISO 2768 is an internationally accepted global standard that specifies tolerance levels for dimensions and geometries, divided into four main grades of tolerances:
F (fine): Suited for parts with high precision requirements such as those found in aerospace and electronics industries. M (medium): Commonly applied in industrial machinery and automotive sectors, while C and V grades can be found for larger components with less stringent precision requirements.
ISO 2768 encompasses both dimensional tolerances under ISO 2768-1 and geometrical tolerances under ISO 2768-2, providing comprehensive guidance on various tolerance grades based on part size and function.
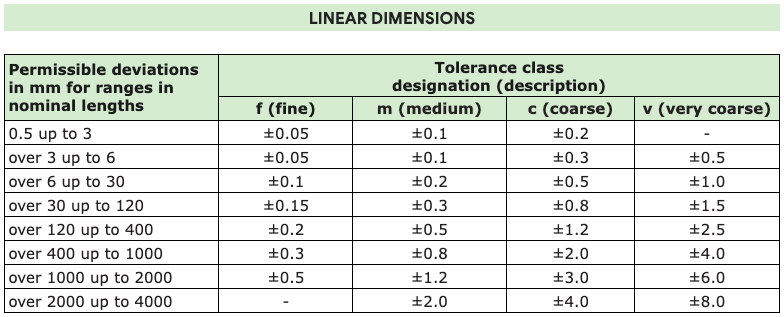
2. DIN 7168: German Tolerance Standard
DIN 7168, the German standard similar to ISO 2768, contains general tolerance grades with slight variations for various applications. It provides fine, medium, coarse and very coarse tolerance grades which assist manufacturers in meeting preciseness requirements in various applications and is commonly employed in German and European manufacturing facilities.
3. ASME Y14.5 GD&T Specification
The ASME Y14.5 standard from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers sets forth precise geometric dimensioning and tolerancing requirements that are widely recognized in North America. Tolerances associated with geometric dimensioning and tolerancing control part shape as well as relative features like flatness, parallelism, and positional accuracy - making this standard particularly suited to high precision parts often found in sectors like aerospace, medical devices and automotive applications.
The standard has some similarity to the ISO standard and is usually divided into several typical accuracy classes:
Tolerance type | Symbol | Allowable Tolerance |
Depth of parallelism | ∥ | 0.01 - 0.1 mm |
Perpendicularity | ⊥ | 0.02 - 0.15 mm |
Coaxiality | Ø | 0.01 - 0.2 mm |
Roundness | Ⓞ | 0.01 - 0.05 mm |
Position | ⌖ | 0.02 - 0.5 mm |
4. China National Tolerance Standard 1184-1996:
China's national tolerance standard GB/T 1184-1996 follows closely to ISO standards while taking into account local production practices. It is widely utilized by Chinese manufacturers and provides consistent tolerance levels across multiple applications.
Tolerance level | Precision Symbol | Size range(mm) | Allowable Tolerance(±mm) |
Refined | f | 0.5 - 3 | 0.05 |
0.08 | |||
0.15 | |||
Center | m | 0.5 - 3 | 0.1 |
0.12 | |||
0.2 | |||
Roughness | c | 0.5 - 3 | 0.15 |
0.2 | |||
0.5 |
Selecting the Appropriate Tolerance Values in CNC Machining Tolerance Selection
Selecting an optimal tolerance level is key to maintaining precision, functionality and production costs in an optimal manner. Here are some factors you should keep in mind when making this choice:
1. Functional Requirements: Components with stringent functional requirements--such as those involving moving parts or operating in high-stress environments--should require tighter tolerances in order to provide optimal performance.
2. Material Properties: Different materials expand and contract differently when exposed to temperature, pressure or other environmental stimuli, so softer materials may require wider tolerances in order to accommodate potential deformation.
3. Manufacturing Capabilities: Tighter tolerances require advanced machinery and experienced operators. CNC machining centers with higher precision may help achieve tighter tolerances; however, additional investment and expertise may be necessary to do this effectively.
4. Considerations of Cost: Tight tolerances can drive up manufacturing costs. Establishing the necessary tolerance levels without over-specifying can help manage these expenses while meeting quality standards.
5. Industry Standards and Specifications: Every industry has specific tolerance standards that must be observed to meet industry-specific specifications. Educating yourself about these stipulations will allow for parts that conform to them being delivered on time for production.

Tip for Managing CNC Machining Tolerances
- Establish Tolerances Early: Establishing tolerances during the design stage can reduce rework and increase manufacturing efficiency.
Wherever Possible, Adopt Standardized Tolerance Grades: When applicable, adopting ISO or ASME tolerance grades (for instance) can greatly streamline production while improving consistency.
Consult With CNC Machining Experts: Experienced machinists can offer valuable insight into achievable tolerances based on part geometry, materials used, and manufacturing capabilities.
Summary
CNC machining tolerances play a pivotal role in parts manufacturing and product assembly, directly impacting on accuracy and quality of products. Achieve maximum service life and reliability from parts, while simultaneously controlling production costs through reasonable tolerance selection. Yixin Precision strictly follows customer specified tolerance standards to deliver more stable quality parts with precise CNC machining tolerances - effectively guaranteeing their machining accuracy in an ever-competitive market environment. Report this page